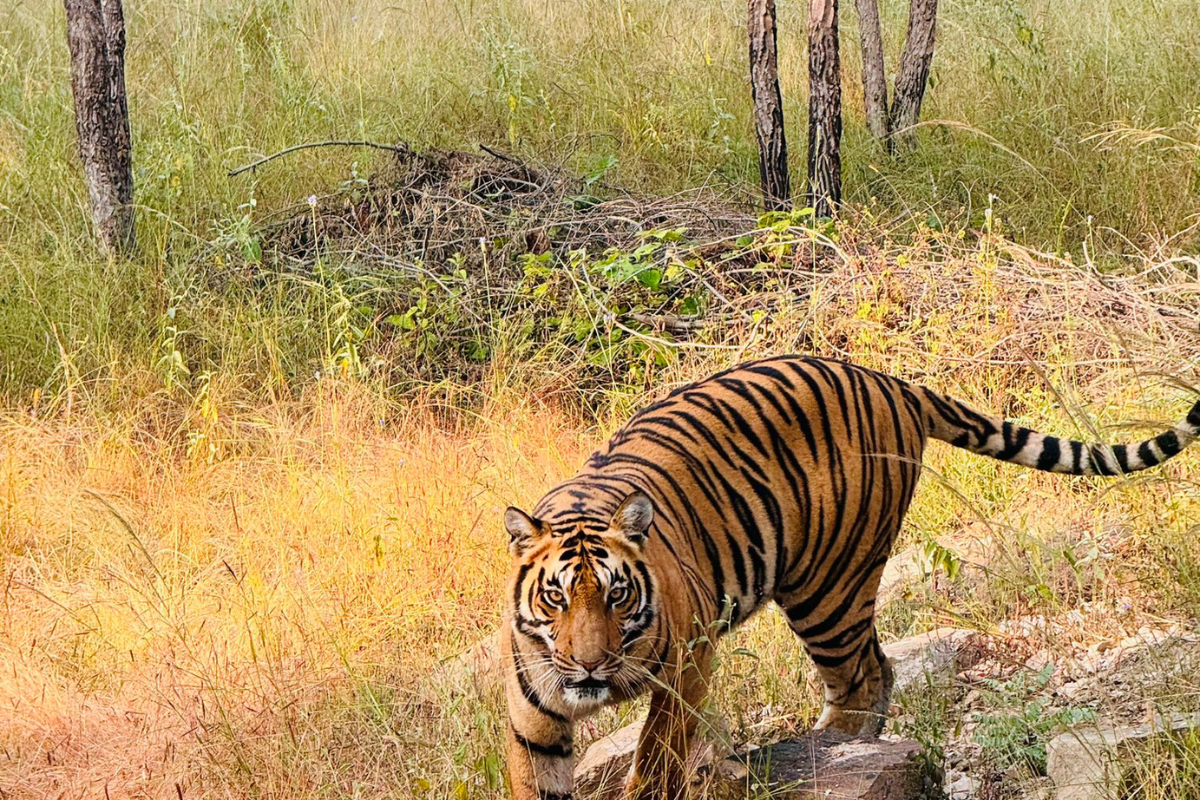
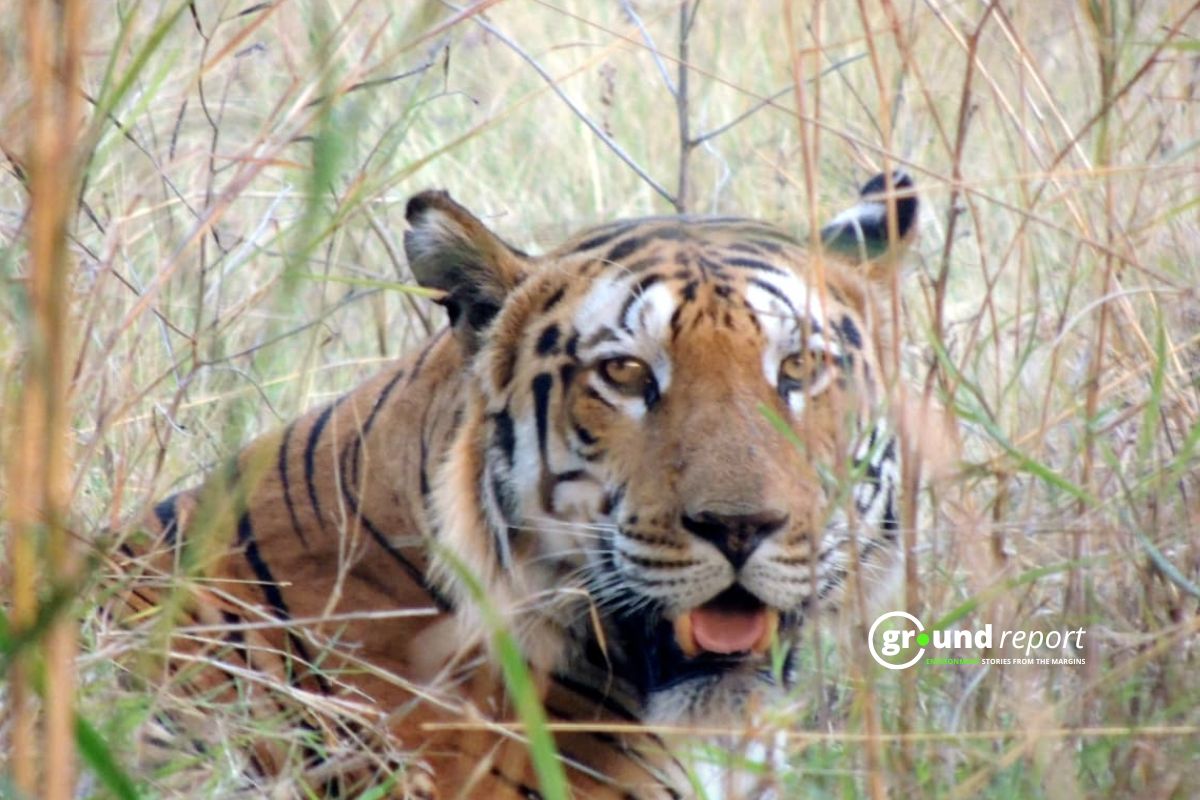
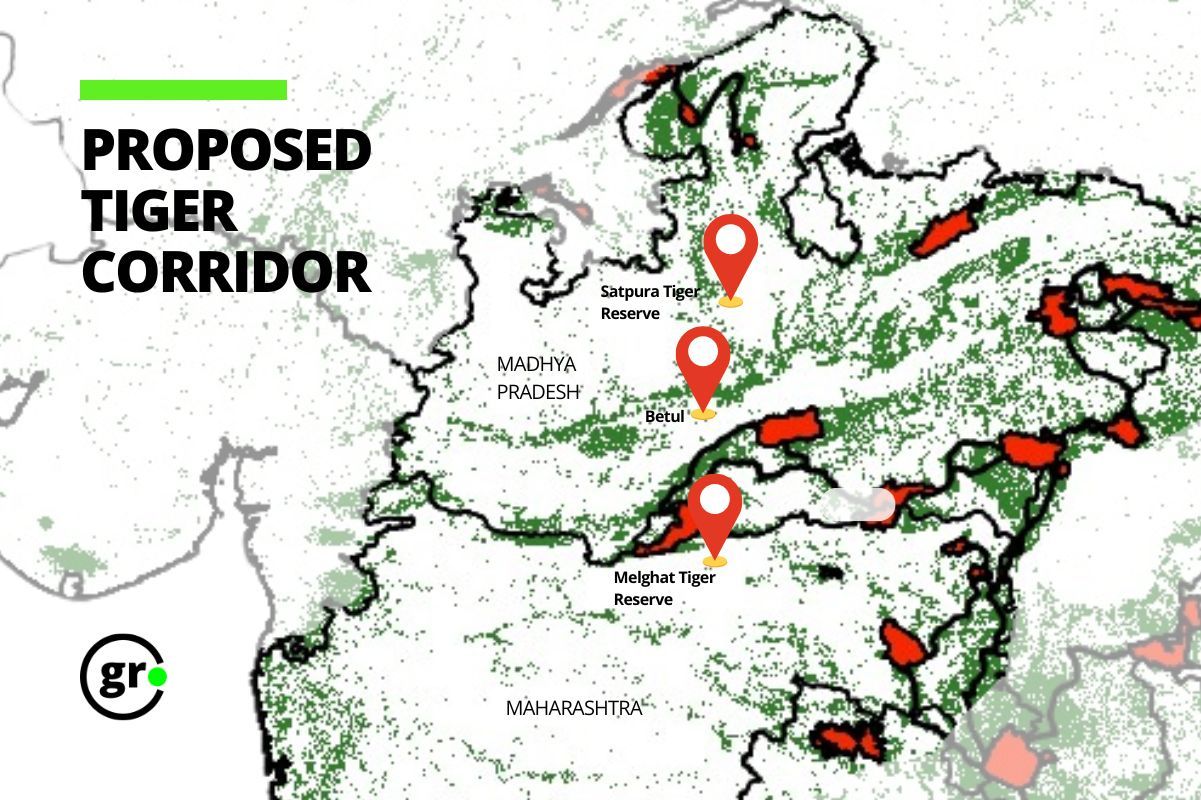
Madhya Pradesh is setting up its first conservation reserve in Betul district, located between Satpura and Melghat Tiger Reserves. This step, supported by the MP Wildlife Protection Board, aims to protect an important wildlife corridor that helps animals move between these two tiger areas.
Chief Minister Mohan Yadav has asked the forest department to quickly prepare a detailed plan for the state government to review. He also highlighted that this conservation reserve is expected to boost tourism in the region.
In a recent meeting of the MP Wildlife Board, Betul MLA Hemant Khandelwal suggested this location. He said that Betul’s forests connect Satpura Tiger Reserve in Hoshangabad district and Melghat Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra’s Amravati district, making it an important wildlife corridor.
The forests in Betul act as a natural path for animals to move between these two reserves. Because of this, it is the most suitable place in Madhya Pradesh for a conservation reserve. Setting up this reserve near the Maharashtra border will also help increase tourism in the area.
Satpura and Kanha’s rich wildlife
Satpura Tiger Reserve in Madhya Pradesh is known for its rich wildlife, including insects, birds, and mammals. To boost tourism while protecting nature, studies have been done to check Madhya Pradesh’s tourism policy around the reserve. Kanha Tiger Reserve, also in Madhya Pradesh, is one of the oldest and best-protected wildlife sanctuaries in Central India. It became part of Project Tiger in 1973–74, showing its importance in saving tigers.
Nestled in the Satpuda hill range in Maharashtra, Melghat Tiger Reserve is known for helping to sustain a sizable tiger population in the state. Studies on the reserve’s biodiversity have concentrated on cataloguing twelve hitherto unidentified species of scarabaeid beetles in the area in 2009–2010.
The finding highlights the ongoing efforts to understand and protect the different animals and plants in Melghat Tiger Reserve. Many bird species also live in the reserve, so regular monitoring and conservation work are needed to keep them safe.
Value & multiple advantages of conservation reserves
Protection of biodiversity and provision of necessary ecosystem services that support environmental sustainability depend much on conservation reserves. Often hosting a great concentration of regional species diversity across several taxa, including birds, plants, amphibians, and small mammals, these reserves provide refuge for a great variety of species.
Apart from their environmental worth, conservation reserves offer a wide range of ecosystem functions directly advantageous for human populations. These services comprise pollination, which is vital for agricultural output; biological pest management, which lessens reliance on dangerous pesticides; and cultural services including recreation, thereby boosting tourism and quality of life.
A community-based co-management model, community reserves and conservation reserves help to promote an inclusive and dispersed method of managed protected areas. This cooperative approach enables local people to actively engage in conservation activities, therefore ensuring that reserve management plans incorporate their traditional knowledge and sustainable practices.
Local stakeholders included in decision-making processes help to promote social fairness, improve conservation results, and instill in community members a feeling of ownership and responsibility.
India’s system of tiger reserves
India features a large network of carefully placed tiger reserves meant to protect their habitats and preserve its famous tiger count. Aiming to guarantee the long-term survival of tiger populations for scientific, economic, artistic, cultural, and ecological goals, Project Tiger, started in 1973, forms the pillar of efforts at tiger conservation in India.
Project Tiger has been especially important in increasing tiger numbers and reducing risks to their survival by means of focused conservation plans and habitat management initiatives. With around 70% of the world’s tigers counted in India today, India’s conservation efforts are clearly successful, and its will to protect this amazing animal for the next generations is evident.
New conservation areas, such as the one suggested in Madhya Pradesh, help India’s attempts to preserve its tiger count and preserve the biological integrity of its varied terrain even further.
Support us to keep independent environmental journalism alive in India.
Keep Reading
NTCA flags tiger habitat risk in MP’s Morand-Ganjal dam project
Tiger sightings near Bhopal’s urban forest raise safety concerns
Tigers, Leopard die of bird flu at Nagpur zoo; red alert issued
Anand Mahindra shares pictures of wildlife corridor built in Pench Tiger Reserve
Follow Ground Report on X, Instagram and Facebook for environmental and underreported stories from the margins. Give us feedback on our email id greport2018@gmail.com.
Don’t forget to Subscribe to our weekly newsletter, Join our community on WhatsApp, and Follow our YouTube Channel









