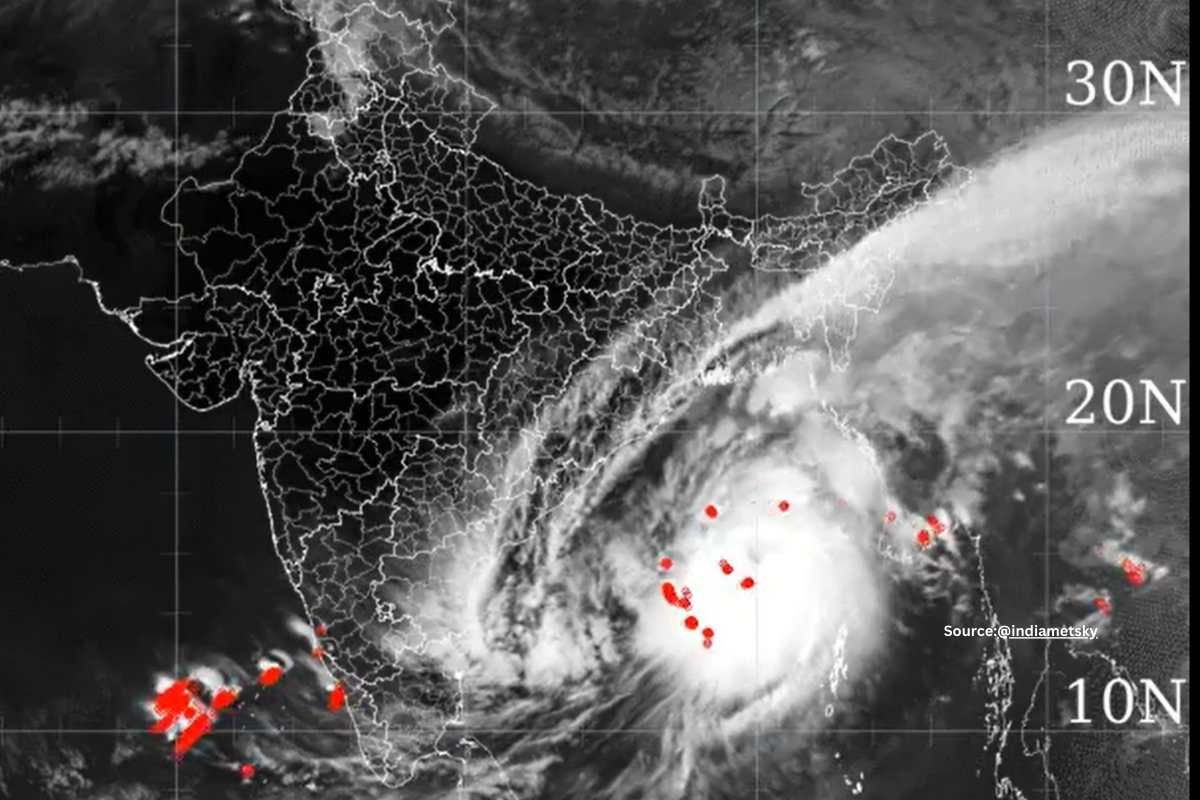
Meteorology, the study of weather, looks at many factors to predict storms and manage disasters. The Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) wave is one important factor. It’s an atmospheric wave that can affect how strong a cyclone gets and how it behaves. Meteorologists and climate scientists study it closely to better understand and forecast cyclones.
The Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) is a significant player in the tropical climate, influencing weather patterns across the globe. It is an eastward moving ‘wave’ of enhanced rainfall that typically recurs every 30 to 60 days. Understanding the MJO is crucial for predicting cyclones because it can modulate the environment in which these storms develop.
Role of MJO in cyclone formation
Cyclones, also known as tropical storms or hurricanes, depend on several factors for their formation, including warm sea surface temperatures, high humidity, and low vertical wind shear. The MJO influences these factors by altering the atmospheric conditions over the tropical oceans. When the MJO is in its active phase, it enhances convection and rainfall, leading to increased thunderstorm activity. This can create a more favorable environment for cyclone development by providing the necessary energy and moisture.
Moreover, the MJO can affect the strength and path of cyclones. During its active phase, the MJO can increase the likelihood of cyclone formation and intensification. Conversely, during its suppressed phase, the MJO can inhibit cyclone development by stabilizing the atmosphere and reducing convection.
The connection between MJO and cyclones lies in the way these waves influence atmospheric conditions. MJO phases are broadly categorized into two types – enhanced convective and suppressed convective phases. During the enhanced convective phase, increased thunderstorm activity and cloud cover occur, creating conditions conducive to cyclone formation and intensification. Conversely, the suppressed convective phase tends to inhibit cyclone development.
Predicting weather and cyclones with MJO
Accurate prediction of the MJO’s phases and intensity is vital for forecasting tropical weather, including cyclones. Meteorologists use various models and satellite data to track the MJO and predict its impact on weather patterns. By understanding the MJO’s current state, forecasters can provide early warnings for potential cyclone formation and advise on preparedness measures.
The influence of the MJO extends beyond the tropics. It can affect monsoon systems, alter jet streams, and even influence weather in temperate regions. For instance, the MJO can modulate the Indian Monsoon, affecting rainfall distribution and intensity, which has significant implications for agriculture and water resources.
Despite its importance, predicting the MJO and its impacts remains a challenge. The MJO is a complex phenomenon that interacts with other climate systems, such as El Niño and La Niña. Researchers continue to study the MJO to improve our understanding and forecasting abilities.
The Madden-Julian Oscillation is a key factor in the formation and behavior of cyclones. Its ability to modulate the tropical atmosphere makes it an essential element in weather prediction. As research progresses, our ability to forecast the MJO and its impacts will enhance our preparedness for cyclones and their potential effects on communities around the world.
Understanding the MJO is not only crucial for predicting cyclones but also for comprehending the broader implications it has on global weather patterns. As we continue to face the challenges of climate change, the study of phenomena like the MJO becomes increasingly important in our efforts to adapt and mitigate its effects. The ongoing research into the MJO and its interactions with other climate systems will undoubtedly contribute to more accurate weather predictions and better-informed decision-making for the future.
Keep Reading
- IMD forecasts above-normal winter temperatures across India
- Drought Map: 23 countries in emergency, including India
- Climate chaos: 2023 breaks records, signaling global climate emergency
- Agricultural disasters cost farmers Rs 10.2 lakh crore every year
Follow Ground Report for Climate Change and Under-Reported issues in India. Connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Koo App, Instagram, Whatsapp and YouTube. Write us on GReport2018@gmail.com.