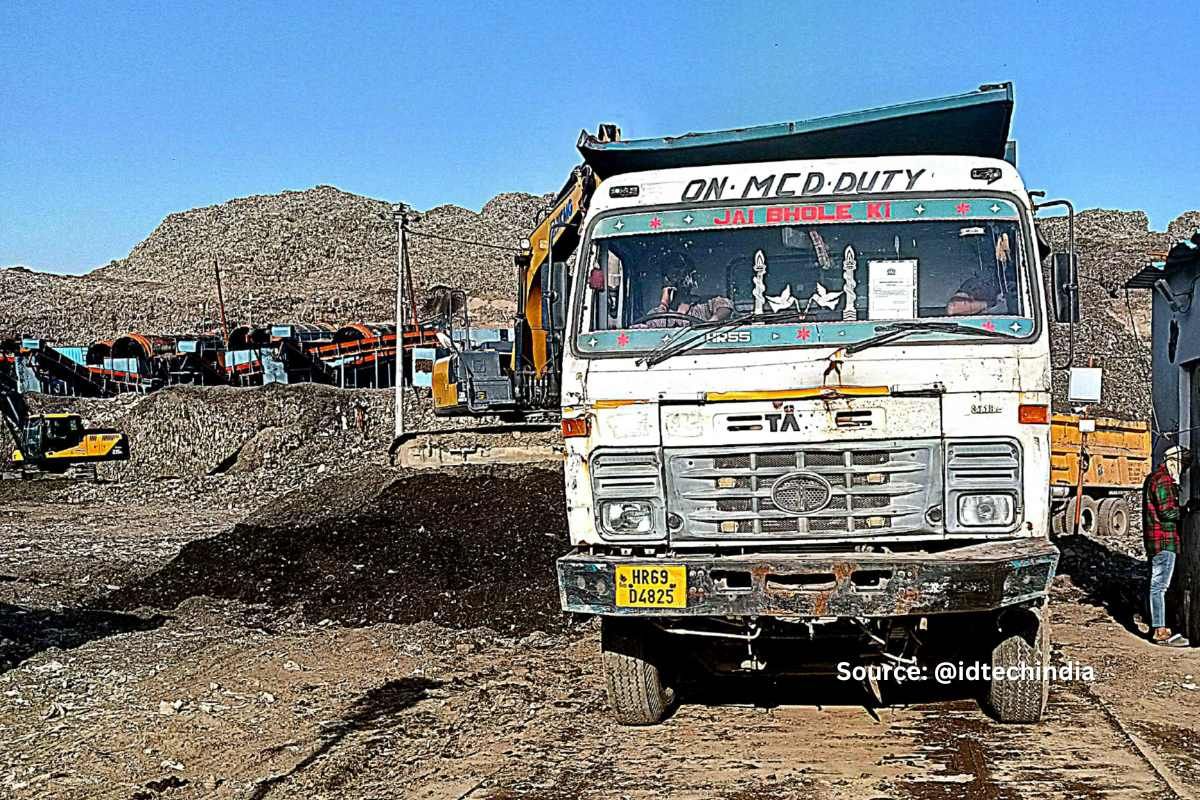
The city of Delhi, India, is one of the most populous cities in the world and generates a vast amount of waste every day. This waste poses a significant challenge to the city’s infrastructure and affects the quality of life of its residents.
The traditional methods of waste disposal, such as landfill and incineration, are no longer viable due to their adverse effects on the environment and human health.
In recent years, there has been an increasing interest in the potential of new technologies, such as bioreactors and plasma gasification, to revolutionize the way Delhi manages its waste.

Bioreactors
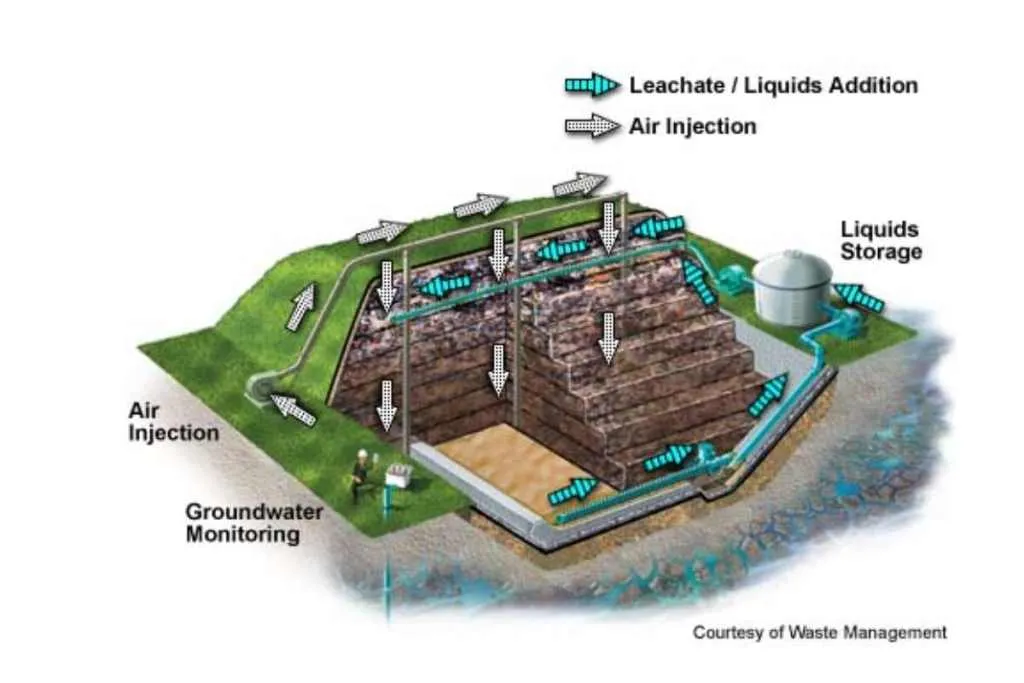
Bioreactors are an innovative waste treatment technology that uses microorganisms to break down organic waste. They are highly efficient, cost-effective, and environmentally friendly. Bioreactors work by creating an optimal environment for microorganisms to thrive, which accelerates the process of decomposition.
The microorganisms consume the organic waste and convert it into biogas, which can be used to generate electricity or fuel. The remaining material, known as dige-state, is a nutrient-rich fertilizer that can be used in agriculture.
Plasma gasification
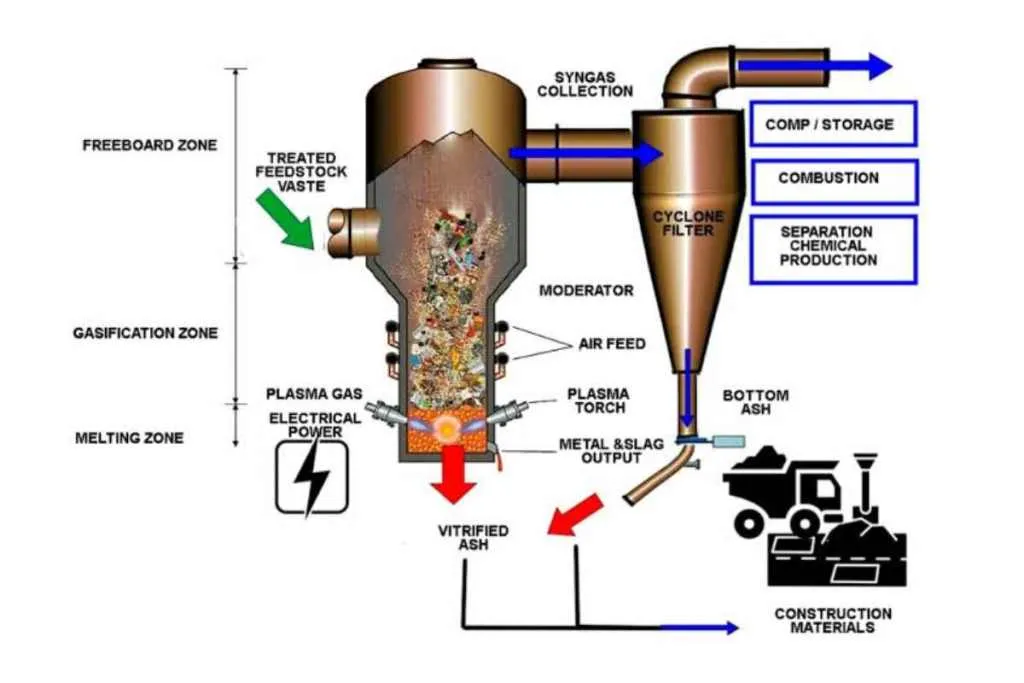
Plasma gasification is another promising technology that can transform waste into valuable resources. This technology uses plasma, a highly energetic gas, to break down waste into its constituent elements. Plasma gasification operates at high temperatures and can handle a wide variety of waste streams, including hazardous waste.
The process of plasma gasification results in the formation of syngas, a mixture of carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which can be used as a fuel or to generate electricity. The remaining material is a glass-like substance, known as slag, which can be used in construction.
Benefits
The potential benefits of bioreactors and plasma gasification in Delhi are significant. These technologies can significantly reduce the amount of waste that ends up in landfills and incinerators, reducing the environmental impact of waste disposal.
It can also generate clean energy and produce valuable resources such as fertilizer and syngas. In addition, bioreactors and plasma gasification may create new opportunities for employment and entrepreneurship in the waste management sector.
However, the wide adoption of these technologies in Delhi also presents some challenges. Initial capital costs to install bioreactors and plasma gasification plants can be high, and the technology requires skilled personnel to operate and maintain them. Moreover, integrating these technologies into existing waste management infrastructure may require overcoming regulatory and institutional barriers.
Despite these challenges, the potential of bioreactors and plasma gasification to revolutionize waste management in Delhi cannot be overstated. These technologies offer a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional waste disposal methods and can create new economic opportunities.
With the right support and investment, bioreactors and plasma gasification can help Delhi manage its waste effectively and create a cleaner, greener, and more sustainable city.
Conclusion
Bioreactors and plasma gasification are innovative waste management technologies that can transform the way Delhi manages its waste. These technologies offer significant environmental and economic benefits. They reduce the amount of waste that goes to landfills and generate clean energy and valuable resources. While there may be challenges to their adoption, with the right support and investment, bioreactors and plasma gasification can help Delhi create a more sustainable and livable city.
Keep Reading
- Korea’s Volume-based waste fee system, Explained!
- What are the rules and regulations to dispose of e-waste in India?
- Increasing landfills pose risks in the Tinsukia district, of Assam
- Bandipora village started solid waste management for the first time
Follow Ground Report for Climate Change and Under-Reported issues in India. Connect with us on Facebook, Twitter, Koo App, Instagram, Whatsapp and YouTube. Write us at GReport2018@gmail.com









